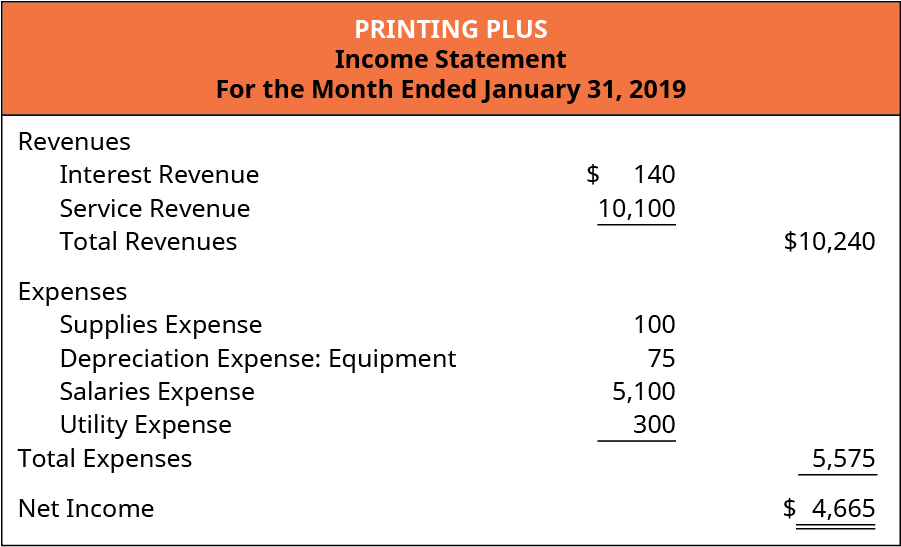
Many companies have interest-bearing assets, such as loans and investments, that generate a stream of income for the company. That interest can be categorized as either “interest receivable” or “interest revenue.” These accounting terms have slightly different meanings. This example illustrates how interest revenue is earned, recognized, and eventually collected.
Interest Income Journal Entry
A company recognizes revenue under that principle by applying a 5-step model as follows. Top 10 differences between IFRS 15 and ASC Topic 606 for revenue recognition. A leveraged buyout (LBO) is a transaction in which a company or business is acquired using a significant amount of borrowed money (leverage) to meet the cost of acquisition.
FAR CPA Practice Questions: Capital Account Activity in Pass-through Entities
For companies in the business of lending money, Interest Revenues are reported in the operating section of the multiple-step income statement. These GAAP differences, combined with the various accounting judgments that often affect the recognition of revenue, mean that revenue and performance from customer contracts may be reported differently across peer companies. Dual preparers and users of financial statements should carefully assess the effect of key differences between IFRS Standards and US GAAP in this area. Businesses record their financial transactions in the books of accounts on the basis o the generally accepted accounting principles (GAAP). A company following GAAP would record both interest revenue and interest receivables in the designated sections of the income statement.
Net interest income
At the same time, it is to record the interest income that the company has earned during the current accounting period. The journal entry at the end of the period is necessary for the company to recognize the revenue that it has already earned. Likewise, the total income and assets will be understated in the financial statements if no necessary adjusting entry is made for the interest income. Under the accrual basis of accounting, the Interest Revenues account reports the interest earned by a company during the time period indicated in the heading of the income statement. Interest Revenues account includes interest earned whether or not the interest was received or billed. Interest Revenues are nonoperating revenues or income for companies not in the business of lending money.
To account for receivable and income, you’ll need nothing more than a good calendar and a basic calculator. Let’s work through a simple example of how to calculate and account for interest receivable and interest revenue for notes receivable. The 360-day-year convention is not used very often anymore since computers have made it easier for banks and companies to calculate interest using actual days (365 or 366, depending on the year). Also, in calculating the due date of a note, start on the day after the date on the note (don’t include that day, but do include the last day).
- No one should act upon such information without appropriate professional advice after a thorough examination of the particular situation.
- IFRS Accounting Standards are, in effect, a global accounting language—companies in more than 140 jurisdictions are required to use them when reporting on their financial health.
- This journal entry will eliminate the $150 of receivable that the company has recorded in the June 30 adjusting entry as well as recognize the 15 days of the interest income that the company has earned in July 2020.
- The unavoidable costs are the lower of the costs of fulfilling the contract and any compensation or penalties from the failure to fulfill it.
Both interest revenue and interest expense are recorded in the income statement. Interest revenue is the interest that an entity earns from the money it has lent or the investments it has made. Suppose Company A lends $500,000 to Company B at an annual interest rate of 6%. The terms of the loan dictate that Company B will repay the interest annually. Vaia is a globally recognized educational technology company, offering a holistic learning platform designed for students of all ages and educational levels. We offer an extensive library of learning materials, including interactive flashcards, comprehensive textbook solutions, and detailed explanations.
US GAAP has no general guidance for recognizing a provision for onerous contracts, but instead the specific recognition and measurement requirements of the relevant Codification Topics/ Subtopics apply. Most companies earn interest income; however, not all of these companies treat interest income as their primary source of income. Therefore, a bank would record interest revenue in the revenue section at the top of the income statement. This interest income earned by the company in the given time period is called interest revenue for the company. Suppose ABC Ltd. is an automobile company with a substantial cash surplus. The company has invested $100,000 in an interest-bearing financial asset, for, say, a certificate of deposits that pays an annual interest rate of 5%.
For the past 52 years, Harold Averkamp (CPA, MBA) hasworked as an accounting supervisor, manager, consultant, university instructor, and innovator in teaching accounting online. For the past 52 years, Harold Averkamp (CPA, MBA) remote tax preparer jobs, work from home online has worked as an accounting supervisor, manager, consultant, university instructor, and innovator in teaching accounting online. Everything you need to know to calculate an interest rate with the present value formula.
The company can make the interest income journal entry by debiting the interest receivable account and crediting the interest income account. In this case, your company will need to account for accrued interest revenue on Dec. 31, 2015, to close out the books for the month and year, well before the note comes due on Feb. 8, 2016. This happens frequently in accrual accounting — revenue is recognized before it is received in cash. Sales of nonfinancial assets, such as property, plant and equipment (IAS 16), intangible assets (IAS 38) and investment property (IAS 40), are accounted for using the measurement and derecognition guidance of IFRS 15. A bank’s main goal is to increase the net interest income it receives.
For instance, if a bank lends £10,000 to a small business, the principal amount in this case would be £10,000. Interest Revenue can be defined as the earnings generated by a company from its lending or investing activities. Use the RFP submission form to detail the services KPMG can help assist you with. The amendments in the ASU are effective for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2022 for public business entities and December 15, 2023 for all other entities. Sales of a subsidiary or equity method investee are outside the scope of IFRS 15 and in scope of the deconsolidation guidance (IFRS 10 and IAS 28, respectively). KPMG has market-leading alliances with many of the world’s leading software and services vendors.